Soft-tissue injuries inside the mouth can be alarming due to how quickly they bleed and how painful they can feel. From accidental bites to sports impacts and falls, these injuries require prompt attention to protect your oral health. Knowing how to respond to cuts, tears, and gum damage—and understanding the importance of proper tooth care—can prevent complications, infections, and long-term discomfort.
When emergencies happen, being informed helps you act confidently and protect your mouth from further harm.
Why Soft-Tissue Dental Injuries Need Immediate Attention
The mouth contains a high concentration of blood vessels and delicate tissues. Even minor trauma can cause significant bleeding, swelling, and soreness. Without rapid evaluation and professional tooth injury treatment, the affected area may become infected, fail to heal properly, or lead to additional oral complications.
Soft-tissue trauma often involves the lips, cheeks, gums, or tongue, and each area requires specific care to ensure complete recovery.
Common Causes of Soft-Tissue Injuries
Accidents inside the mouth happen more often than people expect. The most frequent causes include:
- Biting down accidentally while chewing
- Sports-related impacts
- Falls or sudden collisions
- Sharp foods or foreign objects
- Improper use of dental tools
- Pre-existing dental misalignments
Understanding these triggers helps you take preventive steps and respond quickly when injuries occur.
Signs You Need Emergency Evaluation
Not every cut heals on its own. Certain symptoms indicate that professional attention is necessary. Seek help if you notice:
- Persistent bleeding
- Deep cuts or tears
- Increased pain after several hours
- Swelling that worsens
- Difficulty moving the lips or tongue
- Visible damage to the gums
- Signs of infection, such as redness or pus
Prompt gum laceration repair prevents deeper tissue damage and reduces the risk of long-term complications.
First Steps to Take After a Soft-Tissue Injury
Immediate at-home care can help stabilize the injury and reduce discomfort before your dental appointment. Recommended first actions include:
1. Control the Bleeding
Apply gentle pressure with sterile gauze to support initial dental bleeding control. Change the gauze if it becomes soaked.
2. Rinse with Warm Salt Water
This helps clean the wound and reduces the risk of infection.
3. Apply a Cold Compress
Ice packs reduce swelling and numb pain, helping you manage discomfort on the way to the dentist.
4. Avoid Hot Foods and Drinks
Heat can worsen swelling and make the injury more painful.
These steps support early healing, but professional care is essential for complete recovery.
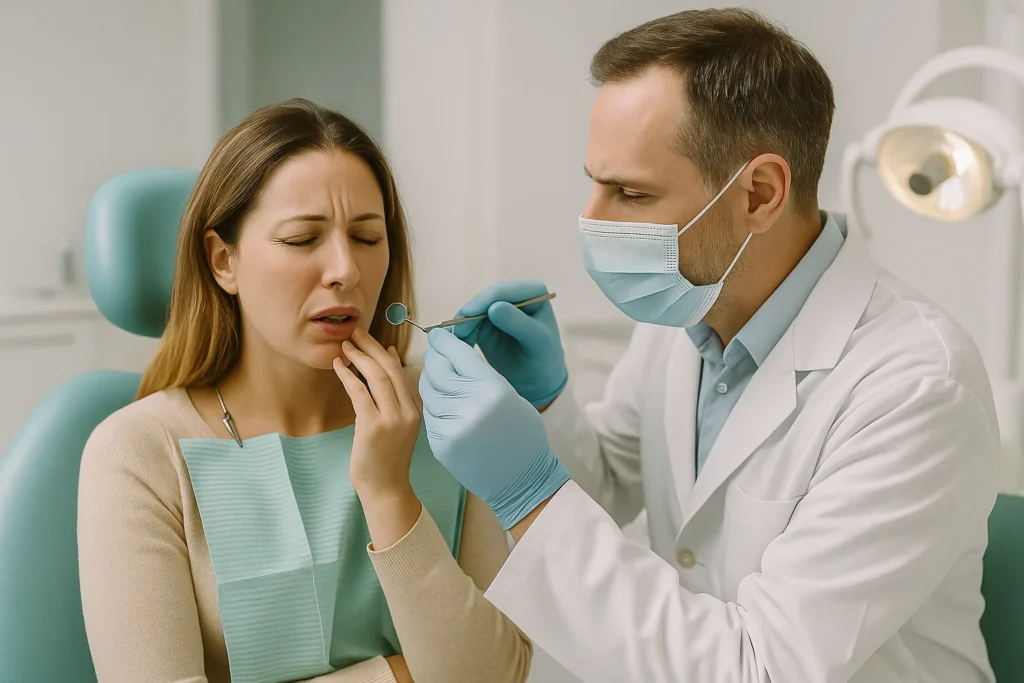

What to Expect During Professional Treatment
Once you arrive at your appointment, the dentist will evaluate the injury using visual inspection and, if needed, diagnostic imaging. Depending on the severity of the wound, mouth treatment may involve:
- Cleaning and disinfecting the injured area
- Sutures for deeper cuts
- Protective coverings or tissue adhesives
- Medication for pain or inflammation
- Evaluation for underlying tooth or bone injuries
Dentists trained in trauma dentistry understand how to properly treat fragile soft tissues while minimizing discomfort and ensuring long-term stability.
Gum Lacerations and Their Unique Challenges
Gum injuries require special attention due to their proximity to the teeth and bone. Proper gum laceration repair ensures that the tissues heal correctly, preventing gum recession, tooth instability, or infection. Immediate evaluation is particularly important if the injury is near the root, as deeper structures may also be affected.
Leaving gum trauma untreated can interfere with oral function and long-term dental health.
Managing Mouth Injuries at Home After Treatment
After receiving professional care, following the dentist’s recommendations helps support healing and reduces complications. Post-treatment guidelines typically include:
- Avoiding spicy, acidic, or crunchy foods
- Keeping the area clean with gentle rinsing
- Taking prescribed medication as directed
- Monitoring for signs of infection
- Avoiding touching or stretching the injured tissue
Proper aftercare is crucial for a complete mouth injury recovery.
Preventing Future Soft-Tissue Trauma
While accidents are sometimes unavoidable, you can reduce the risk by:
- Wearing mouthguards during sports
- Avoiding habits like chewing ice or pens
- Maintaining strong oral hygiene
- Addressing sharp edges on dental restorations
- Managing misaligned teeth that contribute to accidental bites
Protecting the soft tissues supports overall oral health and reduces emergency visits.
Conclusion
Soft-tissue injuries in the mouth may look frightening, but with quick action and informed decision-making, you can protect your oral health effectively. Understanding the importance of compassionate tooth care, recognizing when professional evaluation is necessary, and following proper treatment steps ensures complete healing and long-term comfort. Whether the injury involves bleeding, swelling, or visible tears, prompt care leads to faster recovery and helps maintain a healthy, confident smile.